At its core, cloud computing lets businesses use servers, storage, and software over the internet without owning hardware. It’s pay-as-you-go tech that grows when you need it.
“Cloud spending hit $545 billion in 2022 and will reach $1.3 trillion by 2027, growing 19% yearly,” reports IDC’s latest study.
According to McKinsey, companies that embrace cloud see 20-30% cost savings and launch products twice as fast. From Tesla’s use of AWS for vehicle simulations to Goldman Sachs running risk analysis on Google Cloud, businesses across industries rely on it daily. This guide breaks down what cloud is, why it matters, and how companies use it to win.

2. The Evolution of Cloud Computing
2.1 Historical Development
Cloud computing’s roots trace back to 1960s mainframes at MIT, where multiple terminals shared one computer. The real breakthrough came when Salesforce launched in 1999, proving subscription software worked. Amazon jumped in after facing its own server challenges, launching AWS in 2006. Microsoft Azure followed in 2010, and Google Cloud in 2011. Each brought unique strengths – Amazon’s raw computing power, Microsoft’s enterprise focus, and Google’s data smarts.
Forrester’s 2023 report found 94% of businesses now use multiple clouds, mixing public and private options.
2.2 Technological Advancements of Cloud Computing
Several key tech breakthroughs made cloud possible:
| Technology | Contribution to Cloud Computing |
| Virtualization | Split one physical server into many virtual ones, boosting efficiency by 60-80% |
| High-speed internet | Made remote access practical with under 100ms latency |
| Modern data centers | Warehouses running at 1.1-1.4 PUE vs. 2.5+ for old facilities |
| Containers | Package apps with everything they need to run anywhere |
| Edge computing | Puts cloud power closer to users, cutting response time |
These innovations transformed the cloud from a tech novelty into a business bedrock, powering everything from Netflix streams to bank transactions.
3. Core Components of Cloud Computing
3.1 Infrastructure Fundamentals
Cloud systems run on these key pieces:
| Component | Function |
| Data Centers | Physical buildings with servers, power, and cooling |
| Networking | Connects resources via fiber, routers, and load balancers |
| Storage | Keeps data on SSDs, HDDs, or tape in different formats |
| Servers | Physical or virtual machines that do the actual work |
| Virtualization | Software layer that creates VMs from physical hardware |
| Management Tools | Dashboards and APIs that control it all |
These work together like a utility – available 24/7 and billed based on what you use.
3.2 Virtualization Technology
Virtualization is cloud’s secret sauce. It lets one physical server run many virtual systems, each thinking it has the hardware to itself. This magic trick:
- Turns 15% server utilization into 80%+
- Lets you spin up new servers in minutes, not months
- Keeps workloads separate for security
- Makes recovery from failures automatic
- Cuts energy use drastically
The hypervisor (software like VMware ESXi or KVM) sits between hardware and operating systems, turning physical resources into pools that can be assigned as needed.
4. Cloud Computing Service Models
4.1 Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS gives you raw computing power. Think virtual servers, storage, and networks you control but don’t physically maintain.
Key traits:
| Characteristic | Description |
| Control | You manage the OS and everything above it |
| Scaling | Add/remove resources in minutes with a few clicks |
| Costs | Pay for what you use, often 30-50% cheaper than owning |
| Management Split | Provider handles hardware, you handle software |
Perfect for: Companies with changing workloads, startups avoiding capital expenses, and businesses testing new ideas.

4.2 Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS adds development tools, databases, and middleware on top of infrastructure. It’s the “kitchen” where developers cook up applications without worrying about the “plumbing.”
What you get:
| Feature | Benefit |
| Development Tools | Ready-to-use coding environments with built-in testing |
| Database Services | Managed SQL/NoSQL databases that scale automatically |
| Analytics | Built-in tools for business intelligence |
| Deployment Paths | Push-button publishing from code to production |
PaaS lets developers focus on creating business value instead of managing servers. Studies show it cuts development time by up to 50%.
4.3 Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers complete, ready-to-use applications over the web. Just log in and work – no installation or updates needed.
Benefits include:
| Advantage | Description |
| Accessibility | Work from anywhere on any device with internet |
| Always Current | Updates happen automatically in the background |
| Flexible Pricing | Add/remove users monthly as needs change |
| Integrations | Connect with other cloud tools via APIs |
From Gmail to Salesforce, SaaS has become how most of us use software today. Gartner predicts SaaS will grow twice as fast as infrastructure services through 2026.
5. Cloud Deployment Models
5.1 Public Cloud
Public cloud services run on shared infrastructure available to anyone who signs up. They’re the most common and fastest-growing segment.
Key features:
| Aspect | Details |
| Ownership | Run by providers like AWS, Azure, and Google |
| Resource Sharing | Hardware shared among thousands of customers |
| Costs | No upfront costs, pay only for what you use |
| Scalability | Practically unlimited growth potential |
| Reliability | Multiple data centers ensure 99.9%+ uptime |
Best for: Web apps, email, testing environments, and businesses without strict regulatory requirements.
5.2 Private Cloud
Private cloud gives you cloud benefits with dedicated hardware – either in your data center or hosted for you.
What you get:
| Feature | Benefit |
| Dedicated Hardware | No sharing resources with other companies |
| Total Control | Customize everything to your exact needs |
| Customization | Build exactly what your business requires |
| Security | Physical and logical isolation for sensitive data |
| Compliance | Easier to meet strict industry regulations |
Perfect for: Banks, healthcare providers, government agencies, and others with strict security or compliance needs.
5.3 Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud connects public and private clouds, giving you the best of both worlds.
Advantages:
| Advantage | Description |
| Flexibility | Keep sensitive data private, burst to public when needed |
| Cost Balance | Use cheaper public resources for appropriate workloads |
| Scaling | Handle traffic spikes without building for peak capacity |
| Business Continuity | Back up private systems to public cloud for disaster recovery |
| Migration Path | Move to cloud gradually instead of all at once |
Microsoft research shows 67% of enterprises now use hybrid models, keeping sensitive operations in-house while leveraging public cloud for everything else.

6. Benefits of Cloud Computing for Businesses
6.1 Cost Efficiency
Cloud dramatically changes how businesses pay for IT:
| Cost Factor | Cloud Computing Impact |
| Hardware Costs | Eliminate capital expenses for servers and storage |
| IT Staffing | Reduce system admin needs by 30-50% |
| Energy Bills | Cut power and cooling costs by outsourcing to efficient providers |
| Software Costs | Move from big upfront licenses to monthly subscriptions |
| Financial Flexibility | Convert IT from capital expense to operating expense |
A Deloitte study found businesses save 20-40% when moving from on-premises to cloud infrastructure.
6.2 Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud’s ability to grow and shrink with your needs changes how businesses operate:
| Scalability Factor | Business Benefit |
| On-Demand Resources | Scale up for holiday sales, down when traffic drops |
| Global Reach | Launch in new regions without building data centers |
| Handling Spikes | Survive being featured on TV without your site crashing |
| Dev/Test | Create full testing environments in minutes, delete when done |
| Market Response | Launch new products without guessing capacity needs |
This elasticity ends the days of buying for peak capacity that sits idle 90% of the time.
6.3 Security and Compliance
Major cloud providers now offer security that exceeds what most companies can achieve internally:
| Security Aspect | Cloud Provider Capabilities |
| Data Protection | Military-grade encryption at rest and in transit |
| Access Security | Multi-factor auth, role-based controls, and audit logs |
| Threat Monitoring | 24/7 security operations centers with AI-powered detection |
| Physical Security | Biometric access, guards, and multiple security zones |
| Compliance | Certifications for HIPAA, PCI, SOC 2, ISO 27001, and more |
Cloud providers invest billions in security that would be impossible for most companies to match internally. AWS alone has over 300 security controls.
6.4 Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Cloud-based recovery solutions have transformed how businesses handle disruptions:
| Disaster Recovery Feature | Operational Impact |
| Automated Backups | Set-and-forget protection with point-in-time recovery |
| Geographic Redundancy | Data copied across multiple regions automatically |
| Fast Recovery | Resume operations in minutes instead of days |
| Regular Testing | Test recovery without disrupting production |
| Affordability | Enterprise-grade DR at a fraction of traditional costs |
These capabilities let companies achieve recovery time objectives (RTOs) measured in minutes rather than days.
7. Cloud Computing Applications Across Industries
7.1 Automotive Industry Solutions
Auto companies use cloud to transform everything from design to driving:
| Application Area | Cloud Computing Value |
| Supply Chain | Track parts from factory to assembly in real time |
| Connected Vehicles | Process terabytes of sensor data from millions of cars |
| Factory Analytics | Use manufacturing intelligence to cut defects by 50%+ |
| Customer Experience | Deliver personalized car shopping and ownership apps |
| R&D | Run crash simulations in hours instead of weeks |
Solutions like DataLynx Online help auto service shops manage operations across locations while slashing paperwork.

7.2 Financial Services Applications
Banks and financial firms lead cloud adoption for many critical functions:
| Financial Service Area | Cloud Implementation |
| Customer Data | Create single customer views across products and channels |
| Risk Management | Run complex scenarios in minutes vs. overnight |
| Fraud Prevention | Spot suspicious transactions in milliseconds |
| Trading Systems | Power analytics for traders with sub-second response |
| Compliance Reporting | Automate regulatory filings that once took weeks |
Financial institutions need specialized providers who understand both finance and technology, like those serving the financial services sector.
7.3 Healthcare Innovations
Healthcare organizations use cloud to improve care and cut costs:
| Healthcare Application | Cloud-Enabled Capability |
| Patient Records | Share medical data securely between providers |
| Diagnostic Imaging | Store and analyze MRIs, CT scans, and X-rays affordably |
| Remote Care | Enable video visits and remote monitoring |
| Health Analytics | Spot trends across thousands of patients |
| Medical Research | Share data securely between institutions |
Cloud solutions for healthcare organizations must meet strict HIPAA requirements while handling complex health data and workflows.
7.4 Manufacturing Transformation
Manufacturers are using the cloud to drive Industry 4.0 initiatives:
| Manufacturing Use Case | Cloud Benefit |
| Supply Chain Visibility | Track materials and products end-to-end |
| Equipment Maintenance | Predict failures before they happen, cutting downtime 30-50% |
| Quality Assurance | Catch defects in real time with vision systems and analytics |
| Design Collaboration | Share CAD files and collaborate globally |
| Smart Factory | Connect machines, workers, and systems in real-time |
For manufacturing companies, cloud platforms that understand their unique needs deliver the best results through tailored business intelligence strategies.
8. Implementing Cloud Computing in Your Organization
8.1 Assessment and Planning
Start your cloud journey with thorough preparation:
| Planning Element | Key Considerations |
| App Inventory | List all applications and how they connect |
| Workload Analysis | Rate each application’s cloud-readiness |
| Business Case | Calculate TCO and ROI for migration |
| Risk Assessment | Identify security and compliance concerns |
| Migration Approach | Decide which approach works for each application |
Get key stakeholders involved early – IT, finance, and affected business units all need input.
Need help planning your move? Corpim’s professional services team can guide your assessment and planning, ensuring your cloud strategy fits your business goals with minimal disruption.
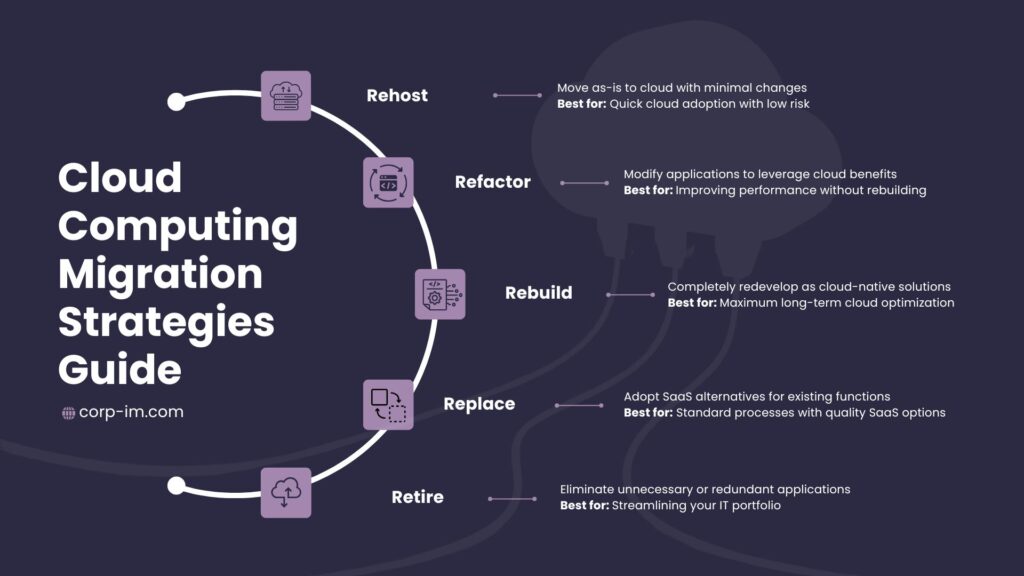
8.2 Migration Strategies
Choose the right approach for each application:
| Migration Strategy | Best Used For |
| Rehost (Lift and Shift) | Legacy apps that work fine as-is |
| Refactor | Apps that need minor changes to work better in cloud |
| Revise | Applications needing significant code updates |
| Rebuild | Apps worth rewriting as cloud-native |
| Replace | Functions better served by SaaS products |
Balance speed, cost, risk, and long-term benefits when choosing your approach.
8.3 Governance and Management
Strong cloud governance prevents problems before they start:
| Governance Area | Implementation Approach |
| Identity Management | Set up who can access what and how |
| Cost Controls | Implement budgets, tagging, and regular reviews |
| Security Rules | Create baseline security standards for all cloud resources |
| Resource Organization | Group resources by project, department, or function |
| Performance Tracking | Monitor application health and user experience |
Companies that skip governance often face surprise bills, security issues, and operational chaos later.
8.4 Optimization and Innovation
Cloud adoption is a journey, not a destination:
| Optimization Area | Business Opportunity |
| Cost Management | Right-size resources and use commitment discounts |
| Performance | Fine-tune applications for better user experience |
| Automation | Replace manual IT tasks with code and workflows |
| Cloud-Native Services | Adopt managed services that eliminate maintenance |
| Data Analytics | Implement AI for business insights |
The real value comes not just from migrating but from continuously improving your cloud approach.
9. Challenges and Considerations in Cloud Computing
9.1 Security Concerns
Address these key security areas in your cloud strategy:
| Security Challenge | Mitigation Approach |
| Data Protection | Encrypt sensitive data and control access tightly |
| Compliance Requirements | Map cloud controls to your regulatory needs |
| Identity Security | Implement zero trust and least privilege access |
| Security Monitoring | Set up comprehensive logging and alerting |
| Vendor Assessment | Verify provider security practices and certifications |
Remember: Cloud providers secure the cloud itself, but you’re responsible for security in the cloud.

9.2 Integration Complexities
Connecting cloud with existing systems creates challenges:
| Integration Challenge | Solution Approach |
| Data Synchronization | Create reliable real-time data flows between systems |
| API Strategy | Build a consistent approach to APIs across environments |
| Network Connections | Implement direct links rather than internet-based connections |
| Identity Systems | Create single sign-on across cloud and on-premises |
| Legacy Connectors | Use integration platforms for older systems |
Pay special attention to integration if you have significant existing IT investments.
9.3 Cost Management
Prevent runaway cloud expenses with proactive management:
| Cost Challenge | Management Strategy |
| Orphaned Resources | Tag everything and regularly audit for unused items |
| Idle Capacity | Shut down development environments when not in use |
| Overprovisioning | Match resource size to actual usage patterns |
| On-Demand Pricing | Use reserved instances for predictable workloads |
| Spending Alerts | Set up notifications before bills get out of hand |
Good cloud computing cost management combines tools and processes to keep spending in check.
10. Future Trends in Cloud Computing
10.1 Edge Computing Integration
Cloud is extending to the edge, closer to users and devices:
| Edge Computing Element | Business Impact |
| Speed | Response times in milliseconds instead of hundreds of ms |
| Data Transfer | Process data locally to reduce bandwidth costs |
| Offline Operation | Keep working when internet connections fail |
| IoT Management | Handle thousands of devices more efficiently |
| Data Sovereignty | Keep data within specific regions as required |
This approach combines cloud scale with local responsiveness, enabling new use cases like autonomous vehicles and smart factories.

10.2 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Cloud providers are democratizing AI access:
| AI/ML Development | Enterprise Application |
| Ready-to-Use AI | Use pretrained models without AI expertise |
| AutoML Tools | Build custom models without data scientists |
| Specialized Hardware | Access GPUs and TPUs without buying them |
| Industry AI Solutions | Deploy prebuilt solutions for common needs |
| AI Operations | Manage models in production environments |
These services let any size company leverage AI business tools without massive investment.
10.3 Serverless Computing Expansion
Serverless architectures continue gaining ground:
| Serverless Benefit | Organizational Impact |
| Maintenance Reduction | Eliminate server management completely |
| True Pay-Per-Use | Pay only for the milliseconds your code runs |
| Infinite Scaling | Handle any load without planning capacity |
| Developer Focus | Write business logic, not infrastructure code |
| Operational Simplicity | Fewer moving parts means fewer failures |
As these platforms mature, more companies are building new applications entirely serverless.
11. Conclusion
Cloud computing has transformed from a tech experiment to the backbone of modern business. By giving companies flexible access to powerful computing resources, cloud enables innovation, efficiency, and agility at every level.
The question isn’t whether to use the cloud anymore, but how to maximize its value through thoughtful strategy, careful planning, and smart management. Partners with both technical and industry expertise can help you navigate this journey successfully.

As cloud technology evolves, businesses that develop cloud fluency and integrate these capabilities into their operations gain major advantages in innovation, adaptation, and competitive position.
For organizations starting or accelerating their cloud journey, consider partnering with experienced providers like Corpim, who bring both technical expertise and industry knowledge. By combining cloud technology with business process understanding, these partnerships deliver transformative results far beyond simple infrastructure updates.

