What you’ll learn in this article:
- What private cloud computing is and how it actually works
- The significant security and control advantages it offers over other infrastructure models
- How different industries leverage private cloud solutions to solve specific problems
- Why many organizations choose private cloud infrastructure for mission-critical workloads
- How to determine if private cloud computing is right for your business

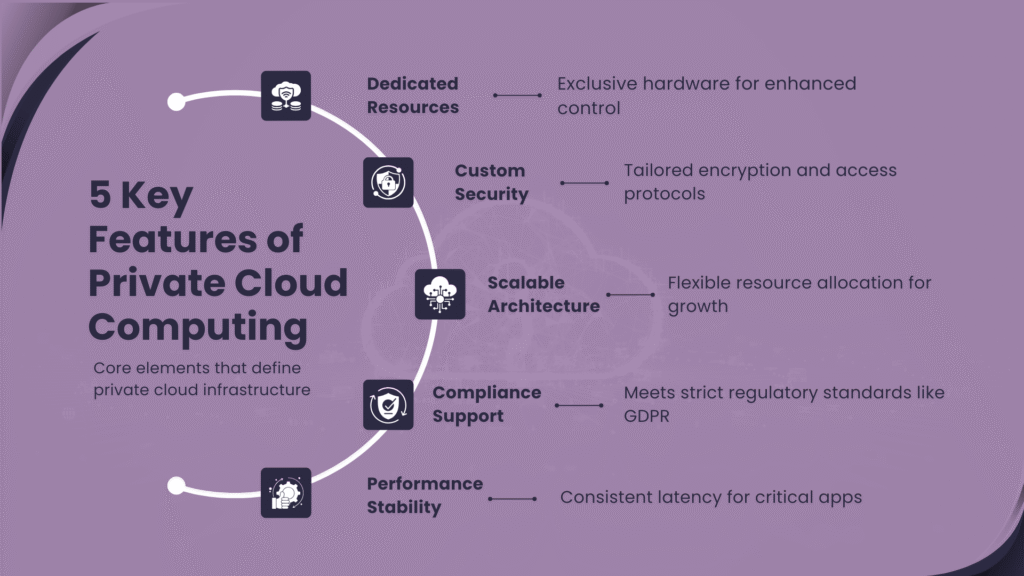
1. What Is Private Cloud Computing?
Private cloud computing delivers cloud infrastructure exclusively operated for a single organization. Unlike public cloud services shared among multiple clients, private clouds provide dedicated resources with enhanced control, customization options, and security benefits. These environments can exist on-premises within an organization’s data center or through third-party hosted services that maintain physical separation from other clients.
| Component | Description | Business Impact |
| Dedicated Infrastructure | Hardware exclusively allocated to one organization | Consistent performance without “noisy neighbor” issues |
| Enhanced Security Controls | Complete oversight of security measures and data location | Reduced risk profile, especially for sensitive information |
| Custom Configuration | Ability to tailor hardware, network, and software to specific needs | Optimized for particular workload requirements |
| Resource Optimization | Advanced virtualization to maximize hardware utilization | Improved ROI on technology investments |
| Self-Service Capabilities | User portals for resource provisioning without IT intervention | Faster deployment cycles and operational agility |
The private cloud market continues to expand, with research firm Gartner reporting that organizations implementing private cloud solutions often cite security (87%), control (79%), and performance (65%) as primary motivators for their choice. This trend reflects the persistent enterprise need for cloud benefits without surrendering oversight of critical systems and data.
2. Private Cloud Computing Models
Private cloud computing encompasses several deployment and management approaches, each offering distinct advantages depending on organizational needs.
On-Premises Private Cloud Options
The traditional private cloud model involves organizations building and managing infrastructure within their own facilities. This approach provides maximum control over hardware selection, configuration, and security protocols. Companies with substantial existing data center investments often prefer this model for its ability to leverage current assets while introducing cloud capabilities.
On-premises deployments typically use enterprise virtualization platforms from vendors like VMware, Microsoft, or open-source alternatives like OpenStack to create resource pools that can be allocated dynamically. These environments require significant internal expertise but offer complete autonomy over the entire technology stack.
| On-Premises Factor | Considerations | Best For |
| Capital Investment | High initial expenditure on hardware and software | Organizations with existing data center space |
| Maintenance Responsibility | Internal teams handle all hardware/software maintenance | Companies with strong IT departments |
| Scaling Timeline | Days or weeks to procure and deploy new hardware | Predictable growth patterns |
| Physical Security | Organization controls all access to equipment | Highly regulated industries requiring chain-of-custody documentation |
| Disaster Recovery | Requires investment in secondary locations | Businesses with multiple facilities |
Hosted Private Cloud Solutions
Hosted private clouds represent a middle ground where dedicated infrastructure is physically located in third-party data centers but remains exclusively allocated to a single customer. This model shifts responsibility for facility management, power, cooling, and physical security to the provider while maintaining logical separation of computing resources.
This approach reduces capital expenditure requirements while still providing many advantages of traditional private cloud computing. Vendors typically offer service level agreements (SLAs) covering availability and performance metrics, giving businesses clearer operational guarantees than self-managed alternatives.
| Hosted Factor | Considerations | Best For |
| Financial Model | Lower upfront costs, predictable operational expenses | Organizations preferring OpEx over CapEx |
| Speed of Deployment | Faster implementation than building on-premises | Projects with tight timelines |
| Management Division | Shared responsibility between provider and customer | Companies with limited facility management capabilities |
| Location Options | Multiple regions available through provider network | Businesses requiring geographic distribution |
| Expertise Required | Less internal staffing for infrastructure support | Organizations focusing IT teams on application development |
Virtual Private Cloud Architecture
Virtual private clouds represent an evolution that uses public cloud infrastructure to create logically isolated environments with many private cloud characteristics. These deployments leverage advanced network segmentation, encryption, and access controls to establish secure boundaries within larger multi-tenant platforms.
While not offering the physical separation of traditional private clouds, VPCs provide comparable security isolation with greater elasticity. This model appeals to organizations needing to balance security requirements with the economic advantages of public cloud scale.
Major providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud offer robust VPC capabilities with features like private subnets, dedicated interconnections, and granular identity management tools that satisfy many enterprise security requirements.
3. Key Benefits of Private Cloud Computing
The choice to implement private cloud computing typically stems from specific organizational needs that public cloud alternatives cannot fully address. These benefits represent strategic advantages that justify the investment required for private infrastructure.
Enhanced Security Framework
Private cloud computing delivers multilayered security advantages that prove especially valuable for organizations handling sensitive data or operating under strict regulatory oversight. By maintaining exclusive control over infrastructure, companies can implement comprehensive security measures aligned precisely with their risk tolerance and compliance obligations.
This control extends beyond software-based protections to include physical access limitations, hardware-level security features, and network isolation that significantly reduces potential attack surfaces. Organizations can implement customized encryption requirements, vulnerability scanning schedules, and patch management processes without navigating the constraints of multi-tenant environments.
| Security Element | Private Cloud Advantage | Business Impact |
| Data Locality | Precise control over where information resides | Compliance with geographic data sovereignty requirements |
| Access Controls | Granular permissions without third-party involvement | Reduced unauthorized access risk |
| Network Security | Complete visibility into all traffic patterns | Earlier threat detection and remediation |
| Customized Monitoring | Security tools tailored to specific application needs | More relevant alerts with fewer false positives |
| Dedicated Resources | No shared components with other organizations | Elimination of multi-tenant vulnerability exposure |
A survey by McKinsey & Company found that 76% of enterprises cite security concerns as the primary factor influencing their private cloud adoption decisions, particularly in financial services and healthcare sectors where data protection carries regulatory implications.
Compliance and Regulatory Alignment
For industries subject to strict regulatory frameworks, private cloud computing creates environments specifically engineered to satisfy compliance requirements. These sectors include financial services (PCI-DSS, SOX), healthcare (HIPAA), government contractors (FedRAMP), and organizations handling European personal data (GDPR).
Private infrastructure allows precise implementation of controls mandated by these regulations, including data residency restrictions, audit mechanisms, and specific security technologies. This capability reduces compliance risk while providing clear documentation for regulatory examinations.
| Regulatory Factor | Private Cloud Implementation | Compliance Benefit |
| Audit Trails | Comprehensive logging across all systems | Complete activity records for examinations |
| Data Residency | Precise control over storage locations | Adherence to geographic restrictions |
| Access Certification | Centralized identity management | Simplified privilege reviews |
| Encryption Requirements | Custom implementation matching specific standards | Documentation of protection measures |
| Separation of Duties | Granular role definitions | Demonstration of control effectiveness |
Organizations report 30% lower compliance-related expenses when using properly configured private cloud environments compared to managing disparate traditional systems or navigating public cloud shared responsibility models.
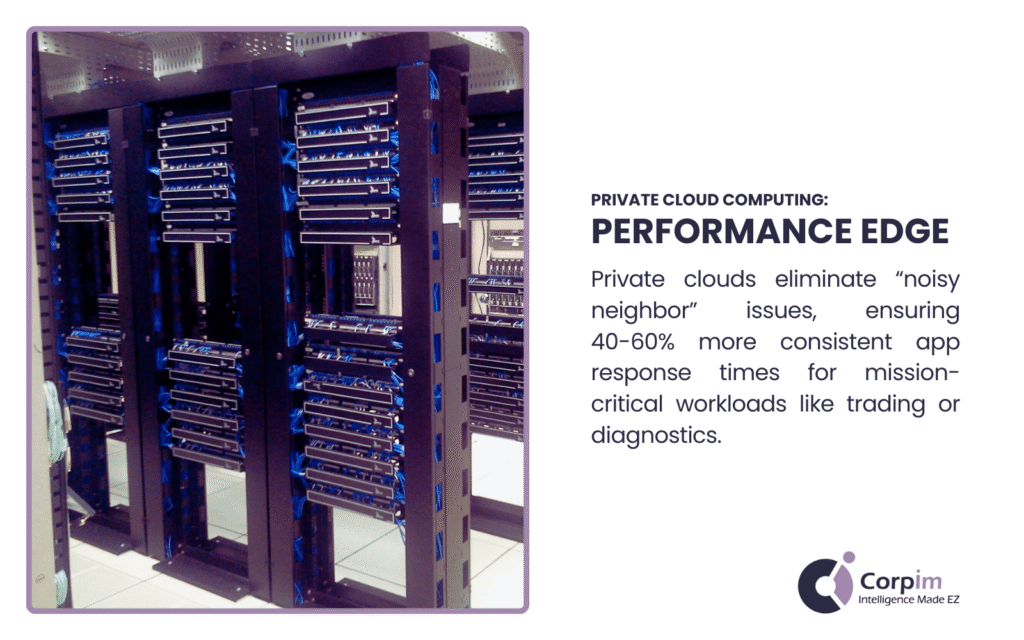
Performance Predictability
Private cloud computing provides consistent, predictable performance characteristics that benefit mission-critical applications with specific resource requirements. By eliminating the “noisy neighbor” effect common in shared environments, private clouds deliver reliable performance even during peak demand periods.
This predictability extends to network latency, storage throughput, and computational capacity—all crucial factors for applications where performance directly impacts business outcomes. Industries like financial trading, manufacturing process control, and healthcare diagnostics particularly value this stability.
| Performance Aspect | Private Cloud Characteristic | Application Impact |
| Compute Resources | Dedicated processing capacity | Consistent transaction processing times |
| Network Latency | Controlled traffic patterns | Reliable real-time operations |
| Storage I/O | Predictable throughput | Stable database performance |
| Resource Contention | Elimination of external competition | Fewer unexpected slowdowns |
| Scaling Control | Planned capacity management | Proactive performance optimization |
Research indicates that applications with stringent performance requirements achieve 40-60% more consistent response times in private cloud environments compared to equivalent public cloud deployments.

4. Private Cloud Computing Implementation Strategies
Successful private cloud deployments require careful planning and execution across multiple technology domains. Organizations must consider infrastructure design, operational models, and migration approaches to maximize return on investment.
Architecture Foundations
The technical foundation of private cloud computing combines several infrastructure layers that together enable the flexibility and efficiency organizations seek. Modern implementations typically incorporate software-defined approaches to maximize automation and resource utilization.
At the hardware level, private clouds require compute servers, storage systems, and networking equipment engineered for virtualization and orchestration. Contemporary designs favor converged or hyperconverged infrastructure that integrates these components into unified systems managed through centralized software interfaces. This approach reduces deployment complexity while improving operational efficiency.
| Infrastructure Layer | Key Components | Design Considerations |
| Compute | Virtualization hosts, container nodes | Processor density, memory capacity, hardware acceleration |
| Storage | Block, file, and object platforms | Performance tiers, data protection mechanisms |
| Network | Software-defined switching and routing | Segmentation capabilities, throughput requirements |
| Management | Orchestration and monitoring tools | Automation interfaces, reporting capabilities |
| Security | Encryption, access control, threat detection | Integration with existing enterprise systems |
Organizations implementing business intelligence strategies often find that private cloud architectures provide ideal platforms for data-intensive analytics workloads requiring both performance and security.
Operational Excellence
Beyond initial deployment, successful private cloud computing environments require mature operational processes that balance technological capabilities with business needs. These practices ensure that cloud resources deliver expected value throughout their lifecycle.
Effective private cloud operations incorporate several key disciplines:
Service Catalog Management: Defining standardized resource offerings that users can request through self-service portals, streamlining provisioning while maintaining governance.
Capacity Planning: Proactively monitoring resource utilization and performance metrics to anticipate future needs before limitations impact business operations.
Cost Transparency: Implementing chargeback or showback mechanisms that attribute infrastructure expenses to specific departments or applications, encouraging responsible resource consumption.
Lifecycle Management: Establishing clear processes for patching, upgrading, and eventually decommissioning components to maintain security and performance.
| Operational Process | Implementation Approach | Business Value |
| Change Management | Automated testing and deployment pipelines | Reduced service disruption risk |
| Incident Response | Integrated monitoring and alerting systems | Faster resolution of operational issues |
| Performance Optimization | Regular capacity reviews and tuning | Improved resource utilization |
| Security Operations | Continuous vulnerability assessment | Proactive risk management |
| Backup and Recovery | Automated protection processes | Reliable business continuity |
Organizations that implement comprehensive business intelligence reporting for their private cloud operations typically achieve 25-30% higher resource utilization rates than those lacking visibility into infrastructure performance.
Migration Pathways to Private Cloud Computing
Moving existing workloads to private cloud environments requires careful planning to minimize disruption while maximizing benefits. Organizations typically approach this transition through phased migration strategies rather than comprehensive “lift and shift” efforts.
Successful migration plans consider application characteristics, interdependencies, and performance requirements to determine appropriate sequencing and transformation approaches. The process typically begins with non-critical workloads to validate infrastructure capabilities before moving to more sensitive systems.
| Migration Approach | Best For | Considerations |
| Rehosting (Lift and Shift) | Legacy applications with limited modification potential | Minimal transformation but limited cloud benefit realization |
| Replatforming | Applications requiring modernization but retaining core functionality | Moderate effort with improved operational characteristics |
| Refactoring | Systems benefiting from cloud-native architecture | Significant development investment with maximum long-term value |
| Replacement | Legacy applications with modern SaaS alternatives | Organizational change management requirements |
| Retention | Specialized systems unsuitable for virtualization | Integration with cloud management frameworks |
Enterprise cloud computing implementations benefit from detailed discovery processes that map application dependencies and performance baselines before migration planning begins.
5. Private Cloud Computing vs. Alternative Models
Understanding how private cloud computing compares to other infrastructure approaches helps organizations determine the optimal deployment model for specific workloads and business requirements.
Private vs. Public Cloud Comparison
While both models deliver computing resources through virtualized, self-service interfaces, significant differences exist in their operational characteristics and value propositions.
| Factor | Private Cloud | Public Cloud |
| Cost Structure | Higher upfront investment, potential long-term savings | Minimal initial cost, consumption-based pricing |
| Control Level | Complete oversight of all components | Limited to service configuration within provider constraints |
| Scalability | Limited by procured capacity | Near-unlimited on-demand resources |
| Security Responsibility | Fully managed by organization | Shared between customer and provider |
| Customization | Extensive hardware and software flexibility | Limited to provider’s service offerings |
| Resource Exclusivity | Dedicated to single organization | Shared underlying infrastructure |
Organizations increasingly adopt public cloud computing for appropriate workloads while maintaining private infrastructure for sensitive applications with specific compliance or performance requirements.
Hybrid Cloud Integration
Many enterprises find that neither pure private nor exclusive public cloud deployments fully address their requirements. This reality has driven significant growth in hybrid cloud architectures that combine multiple deployment models under unified management frameworks.
Hybrid approaches allow organizations to place workloads in optimal environments based on security, performance, and economic factors. Applications can span environments or migrate between them as requirements evolve, creating highly flexible infrastructure ecosystems.
| Hybrid Element | Implementation Approach | Business Value |
| Network Connectivity | Dedicated links between environments | Secure, consistent application communication |
| Identity Management | Federated authentication systems | Seamless user experience across platforms |
| Workload Portability | Container orchestration platforms | Flexibility to move applications as needed |
| Data Synchronization | Managed replication services | Consistent information across environments |
| Unified Monitoring | Cross-platform observability tools | Comprehensive operational visibility |
Successful hybrid integrations require sophisticated data systems modernization to ensure information flows securely and efficiently between private and public environments.
6. Industry Applications of Private Cloud Computing
Different sectors leverage private cloud computing to address specific business challenges while maintaining alignment with regulatory and security requirements.
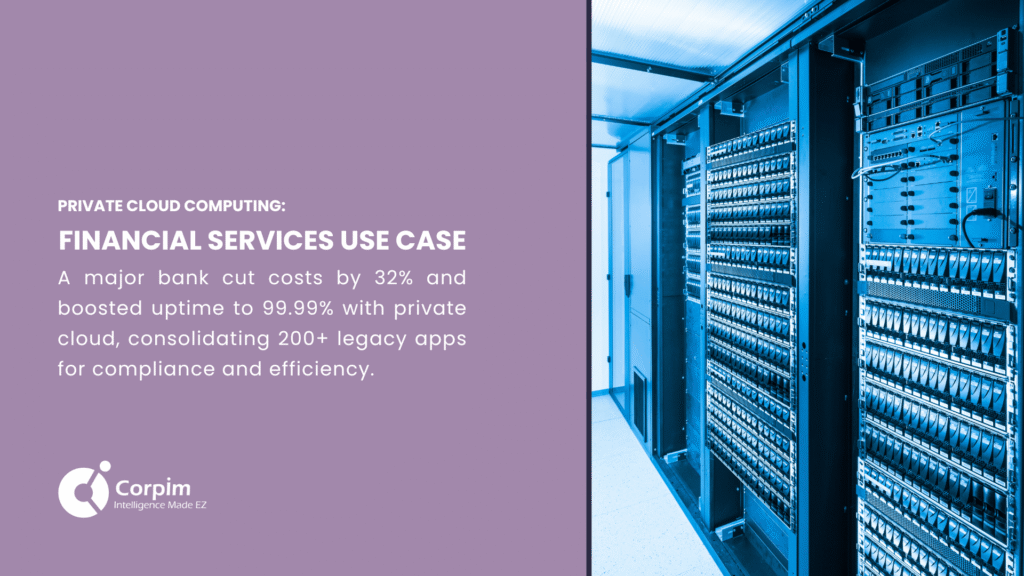
Financial Services Implementation
Banks, investment firms, and insurance companies face stringent regulatory requirements governing data protection, transaction processing, and disaster recovery capabilities. These organizations often implement private cloud computing to modernize infrastructure while maintaining the control necessary for compliance.
Private clouds in financial settings typically support multi-tiered applications with varying performance profiles:
- Core banking platforms and trading systems requiring minimal latency
- Risk modeling and analytics workloads with high computational demands
- Customer-facing digital services requiring both security and scalability
- Regulatory reporting systems with strict data governance requirements
A major financial services institution implemented private cloud infrastructure to consolidate 200+ legacy applications, reducing operational costs by 32% while improving average system availability from 99.9% to 99.99%—representing a significant decrease in downtime for critical customer services.
Healthcare Data Environments
Healthcare organizations face unique challenges balancing technology modernization with patient data protection requirements. Private cloud computing offers a path to improved operational efficiency while maintaining HIPAA compliance and protecting sensitive medical information.
Typical healthcare private cloud implementations include:
| Healthcare Application | Private Cloud Benefits | Compliance Factors |
| Electronic Health Records | Consistent performance for clinical users | Protected health information security |
| Medical Imaging Storage | Scalable capacity for growing imaging data | Data retention policy enforcement |
| Clinical Analytics | High-performance computing for patient insights | Audit controls for data access |
| Telehealth Services | Reliable infrastructure for critical communications | Network security for patient interactions |
| Revenue Cycle Management | Integration with existing healthcare systems | Financial data protection |
For healthcare providers, private cloud computing creates environments that satisfy both technical performance needs and the strict regulatory frameworks governing patient information.
Manufacturing Operations
Modern manufacturing relies increasingly on data-driven systems for production control, quality assurance, and supply chain management. Private cloud computing provides the foundation for these critical operational technologies while addressing concerns about intellectual property protection and shop floor system reliability.
Manufacturing implementations typically emphasize edge computing capabilities that extend private cloud services to production environments, enabling real-time processing with minimal latency. These hybrid architectures connect operational technology (OT) systems with enterprise IT while maintaining appropriate security boundaries.
| Manufacturing Use Case | Private Cloud Implementation | Business Outcome |
| Production Monitoring | Edge nodes connected to central private cloud | Real-time visibility with 99.99% availability |
| Quality Control Systems | Dedicated compute resources for vision systems | Consistent inspection performance |
| Digital Twin Platforms | High-performance simulation environments | Accurate predictive maintenance |
| Supply Chain Integration | Secure gateway services to trading partners | Reduced inventory through improved visibility |
| Product Design Collaboration | High-speed storage for engineering data | Protected intellectual property |
Manufacturing organizations leveraging private cloud computing report 28% faster time-to-market for new products through improved collaboration while maintaining security for proprietary designs.
7. Cost Considerations for Private Cloud Computing
Effective financial analysis of private cloud investments requires understanding both direct expenses and longer-term economic impacts. Organizations must evaluate these implementations through comprehensive cost models rather than simple infrastructure comparisons.
Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
Private cloud computing economics differ significantly from traditional IT approaches and public cloud alternatives. The financial profile typically includes higher initial investment offset by greater control over long-term operational expenses and asset utilization.
A comprehensive TCO analysis should include:
| Cost Category | Components | Optimization Opportunities |
| Capital Expenses | Hardware acquisition, data center facilities, software licensing | Converged infrastructure, open-source platforms, capacity planning |
| Operational Costs | Power, cooling, maintenance, support contracts | Energy-efficient hardware, automation, predictive maintenance |
| Staffing Requirements | Administration, engineering, security operations | Cross-training, automation, managed services |
| Lifecycle Management | Upgrades, replacement cycles, decommissioning | Extended warranties, incremental refresh strategies |
| Business Impact | Application performance, availability metrics, time-to-market | Service level optimization, self-service capabilities |
Organizations partnering with experienced professional services teams typically achieve 15-20% lower TCO through optimized architecture and operational process design.
Economic Benefits Beyond Infrastructure
The business case for private cloud computing extends beyond direct infrastructure costs to include broader operational and strategic advantages that impact overall enterprise performance.
These benefits include:
Risk Reduction: Quantifiable decreases in security incidents, compliance violations, and service disruptions that translate to avoided costs and reputational protection.
Operational Agility: Faster provisioning capabilities that accelerate development cycles, reducing time-to-market for new products and services.
Resource Optimization: Improved utilization of computing assets through virtualization and automation, maximizing return on technology investments.
Staff Productivity: Reduction in manual processes through automation, allowing IT personnel to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine maintenance.
Organizations implementing comprehensive enterprise performance management frameworks can measure these benefits through improved key performance indicators across technical and business dimensions.
8. Future Trends in Private Cloud Computing
The private cloud landscape continues evolving as new technologies emerge and enterprise requirements change. Several trends are shaping the next generation of private cloud implementations.
Containerization and Microservices
Modern private cloud architectures increasingly incorporate container technologies like Kubernetes to support microservices-based applications. This approach improves resource efficiency while providing greater application portability between environments.
Container platforms introduce new operational models that blur traditional boundaries between development and infrastructure teams, enabling DevOps practices within private cloud environments. Organizations adopting these technologies typically achieve 2-3x higher deployment frequency while maintaining security and governance requirements.
The integration of AI in business intelligence systems with containerized applications creates powerful analytical capabilities that can process operational data in real time while maintaining the security benefits of private infrastructure.
Edge Computing Integration
As organizations deploy more systems outside traditional data centers—in retail locations, manufacturing facilities, and field operations—private cloud architectures are extending to include edge computing capabilities. These distributed environments maintain centralized management while processing data closer to its source.
Edge-enabled private clouds address latency requirements for time-sensitive applications while reducing bandwidth consumption for data-intensive workloads. This model proves particularly valuable for organizations with geographically dispersed operations requiring consistent application experiences across locations.
| Edge Integration Element | Implementation Approach | Operational Benefit |
| Local Processing | Standardized compute nodes at remote locations | Reduced latency for critical applications |
| Central Management | Unified orchestration across all environments | Consistent security and governance |
| Data Synchronization | Intelligent replication based on business rules | Optimized network utilization |
| Failover Capabilities | Autonomous operation during connectivity issues | Improved service reliability |
| Security Architecture | Zero-trust models with local enforcement | Protection for distributed assets |
Automotive companies utilizing industry-specific solutions particularly benefit from edge-integrated private clouds that connect dealership operations with central business systems.
AI-Powered Operations
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are transforming how private clouds are managed, introducing predictive capabilities that improve reliability while reducing operational overhead. These systems analyze patterns across infrastructure components to identify potential issues before they impact services.
AI operations (AIOps) platforms continuously monitor performance metrics, log data, and user activities to establish behavioral baselines and detect anomalies. This approach enables proactive maintenance while providing deeper insights into resource utilization and application performance.
| AIOps Capability | Private Cloud Application | Operational Impact |
| Anomaly Detection | Identifying unusual system behavior | Earlier problem resolution |
| Capacity Forecasting | Predicting resource requirements | Proactive scaling decisions |
| Intelligent Alerting | Correlating events across systems | Reduced alert fatigue |
| Performance Optimization | Recommending configuration changes | Improved resource utilization |
| Security Analytics | Detecting potential threats | Enhanced protection posture |
Organizations implementing business intelligence data strategy frameworks with AI capabilities report 40-50% reductions in mean time to resolution for infrastructure incidents.
9. Implementing Your Private Cloud Strategy
Successful private cloud computing implementations require careful planning, appropriate expertise, and ongoing operational commitment. Organizations considering this approach should follow structured methodologies to maximize value while minimizing deployment risks.
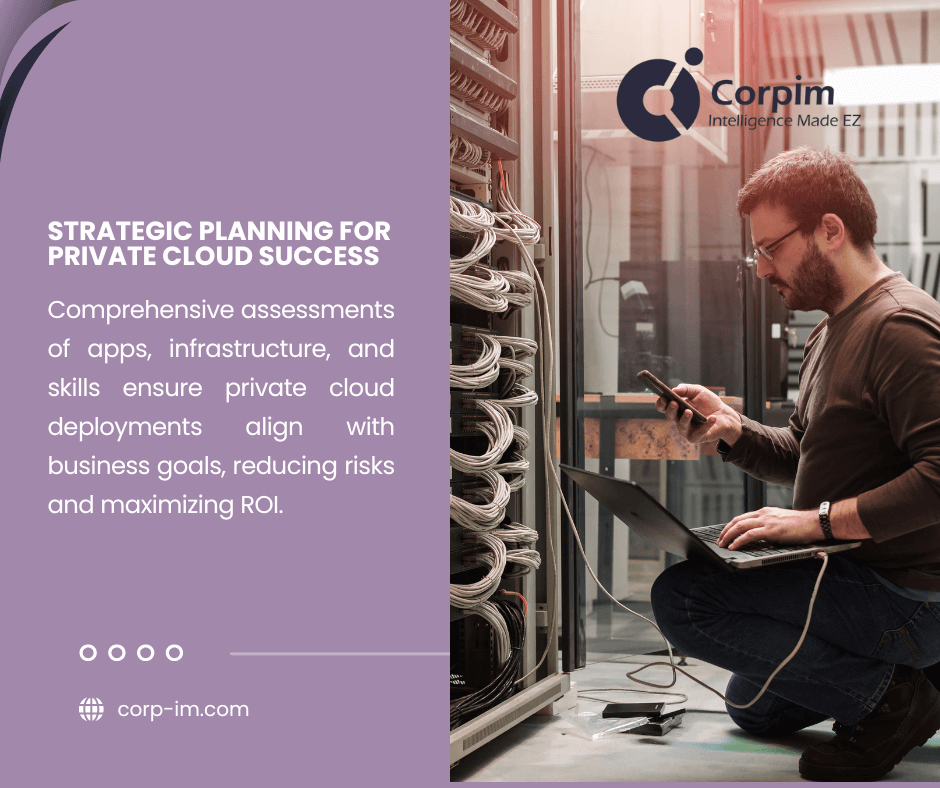
Assessment and Planning
Before implementing private cloud infrastructure, organizations should conduct comprehensive assessments of current environments, future requirements, and organizational readiness. This discovery process establishes baseline metrics while identifying potential challenges that might impact deployment success.
Key assessment areas include:
Application Portfolio Analysis: Evaluating existing systems for cloud suitability, including dependencies, performance requirements, and security considerations.
Infrastructure Capacity Planning: Determining compute, storage, and network requirements based on current usage patterns and projected growth.
Operational Process Review: Assessing existing IT practices against cloud management requirements to identify necessary procedural changes.
Skills Assessment: Evaluating team capabilities relative to new technology requirements, and identifying training or staffing needs.
Organizations working with experienced cloud computing consultants typically achieve more accurate assessments that lead to better-aligned implementation strategies.
Selecting the Right Technology Partners
Private cloud computing implementations often combine components from multiple vendors, making partnership selection a critical success factor. Organizations should evaluate potential technology providers based on several criteria:
| Partner Evaluation Factor | Assessment Questions | Importance |
| Technology Alignment | Does the solution architecture match current and future requirements? | High |
| Support Capabilities | What operational assistance is available during and after implementation? | Critical |
| Integration Experience | Can the partner demonstrate successful deployments in similar environments? | Medium |
| Financial Stability | Is the vendor positioned to provide long-term support for their solutions? | Medium |
| Ecosystem Relationships | Does the partner maintain relationships with complementary technology providers? | High |
Working with specialized data systems modernization partners can accelerate implementation while reducing technical risk through proven methodologies and experienced personnel.
Real-World Success With Private Cloud Computing
Organizations across industries have achieved significant business outcomes through well-executed private cloud strategies. These examples demonstrate the transformative potential of these environments when properly aligned with business objectives.
Case Study: Insurance Provider Transformation
A mid-size insurance company facing aging infrastructure and increasing data analytics requirements implemented a converged private cloud solution to consolidate disparate systems while improving operational capabilities. The project delivered several key outcomes:
- 42% reduction in infrastructure operational costs through improved automation
- 68% faster provisioning for new application environments
- 99.99% availability for customer-facing policy management systems
- Compliance documentation preparation time reduced from weeks to days
- Data analytics processing capacity increased 300% without additional facility requirements
This insurance industry transformation demonstrates how private cloud computing can address both technical debt and future capability requirements within a single strategic initiative.
Case Study: Manufacturing Data Integration
A global manufacturing organization implemented private cloud infrastructure to support increasing data collection from production equipment while maintaining strict security separation between operational technology and business systems. The solution architecture included:
- Edge computing nodes deployed at 24 production facilities
- Central private cloud for aggregation and analytics processing
- Secure integration with supply chain partners through API gateways
- Real-time monitoring dashboards for production status
The implementation reduced unplanned downtime by 37% through predictive maintenance capabilities while improving inventory accuracy by 28% through better production tracking.
Key Takeaways
- Private cloud computing provides organizations with dedicated infrastructure that combines cloud flexibility with enterprise control requirements
- Implementation success depends on comprehensive planning across technology, operational, and organizational dimensions
- Security and compliance advantages make private clouds particularly valuable for regulated industries and sensitive data environments
- Economic benefits extend beyond direct infrastructure costs to include operational efficiency and risk reduction
- Future private cloud environments will increasingly incorporate edge computing, containerization, and AI-powered operations
- Selecting appropriate technology and implementation partners significantly impacts project outcomes
Ready to Transform Your Infrastructure?
If your organization faces challenges balancing modern technology requirements with security, compliance, or performance needs, private cloud computing may provide the optimal solution. Corpim’s solutions architecture team specializes in designing and implementing custom private cloud environments tailored to specific business requirements.
Our approach begins with a comprehensive assessment of your current infrastructure, application portfolio, and operational models to develop architectures that maximize business value while minimizing implementation risks. Through our DataLynx Online platform, we can further enhance your private cloud with industry-specific analytics capabilities that transform operational data into actionable business intelligence.
Contact our professional services team today to discuss how private cloud computing can address your specific business challenges while positioning your organization for future growth.

